
The Linux ocean is rich in distributions. Therefore we need technologies that help us dive into it and discover its different distributions before installing them physically.
Among the technologies that facilitate such a process is virtualization software.
Among the technologies that facilitate such a process is virtualization software.
This article is sponsored by TUXEDOComputers, a German company that produces Linux hardware, notebooks, computers, and more. Always and forever, all ideas and opinions on this website are wholly mine, as my values are not for sale. To learn more, read our Code of Ethics.{alertInfo}
{tocify} $title={Table of Contents}
What is virtualization?
I won't go into details as I will try to simplify the concept as much as possible.
The main goal of virtualization technology is to reduce energy waste and hardware costs by dividing computer resources, such as processor cores, for example, in a way that allows the creation of digital machines to run multiple OSes independently and simultaneously on the same computer. It is possible thanks to virtualization software.
Like all software, virtualization software is either open-source or proprietary.
What is the top open-source virtualization software?
I know the pain of searching for the appropriate applications that a Linux user may suffer from, so this is my list of the best open-source virtualization software that features a usable GUI.The applications mentioned below are available on most Linux distributions (Ubuntu, Arch, Fedora, etc.), and you can easily install them using your system Software Center.{alertInfo}
Oracle VirtualBox

Developed by Oracle, VirtualBox is a free cross-platform (Linux, macOS, Windows) x86 virtualization software. It offers numerous features, like shared folders, 3D acceleration, drag and drop, multiscreen resolutions, USB device redirection (access the USB devices in the virtual machine), and EFI mode. It also supports full ACPI (hardware configuration and power control) and does not require hardware virtualization capability.
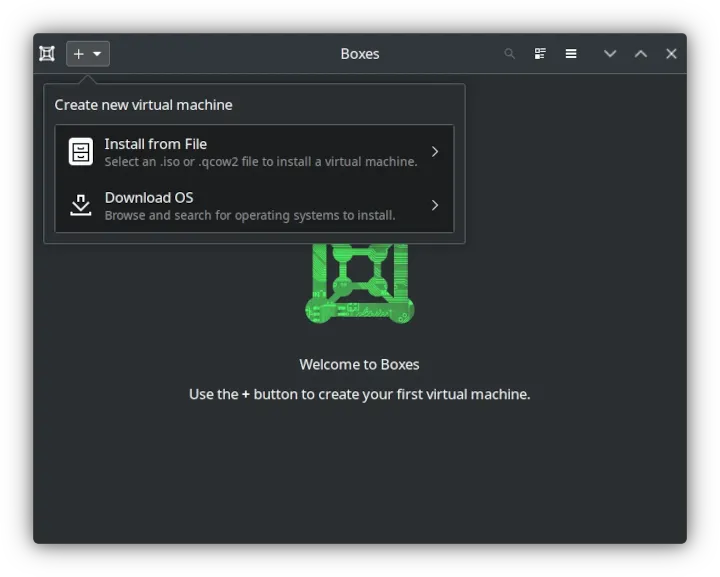 GNOME Boxes is a GTK Linux app based on the QEMU, KVM, and libvirt virtualization technologies. It has a modern minimalistic GUI and offers many features, including but not limited to download and automatic installation of a dozen Linux distros, 3D acceleration, USB device redirection, shared clipboard and folders, and drag and drop.
GNOME Boxes is a GTK Linux app based on the QEMU, KVM, and libvirt virtualization technologies. It has a modern minimalistic GUI and offers many features, including but not limited to download and automatic installation of a dozen Linux distros, 3D acceleration, USB device redirection, shared clipboard and folders, and drag and drop.
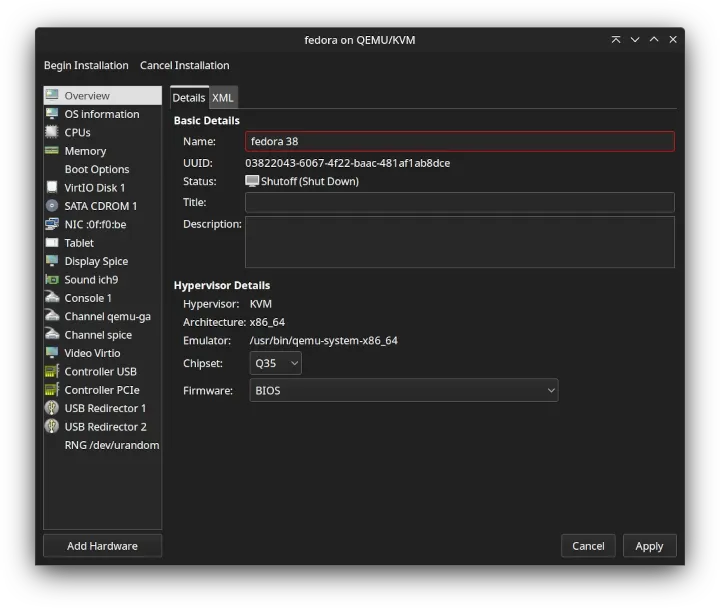
GNOME Boxes
 GNOME Boxes is a GTK Linux app based on the QEMU, KVM, and libvirt virtualization technologies. It has a modern minimalistic GUI and offers many features, including but not limited to download and automatic installation of a dozen Linux distros, 3D acceleration, USB device redirection, shared clipboard and folders, and drag and drop.
GNOME Boxes is a GTK Linux app based on the QEMU, KVM, and libvirt virtualization technologies. It has a modern minimalistic GUI and offers many features, including but not limited to download and automatic installation of a dozen Linux distros, 3D acceleration, USB device redirection, shared clipboard and folders, and drag and drop.Virtual Machine Manager (Virt-manager)

Developed by Red Hat, Virt-manager allows Linux users to create and edit virtual machines using the KVM, Xen, or QEMU open-source technologies. Virt-manager offers almost the same features as VirtualBox and Boxes but, unfortunately, with an outdated GUI (You may have a different opinion).
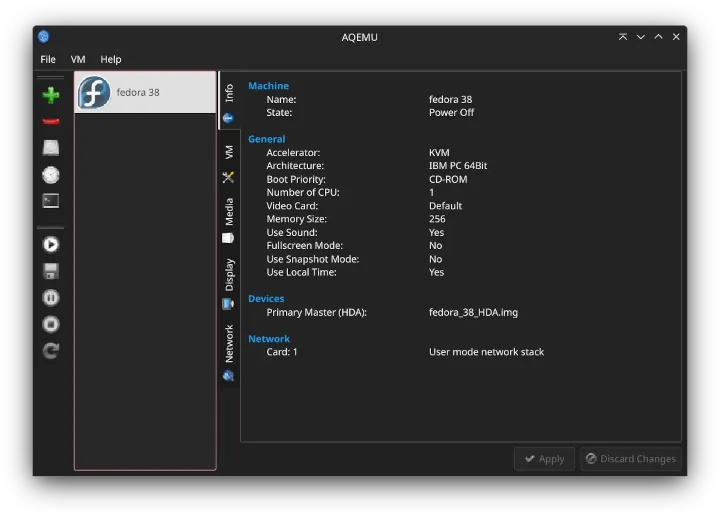 AQEMU is another free and open-source frontend (GUI) for QEMU. The program uses qt5 to provide a simple and efficient interface for creating and configuring virtual systems.
AQEMU is another free and open-source frontend (GUI) for QEMU. The program uses qt5 to provide a simple and efficient interface for creating and configuring virtual systems.
AQEMU
 AQEMU is another free and open-source frontend (GUI) for QEMU. The program uses qt5 to provide a simple and efficient interface for creating and configuring virtual systems.
AQEMU is another free and open-source frontend (GUI) for QEMU. The program uses qt5 to provide a simple and efficient interface for creating and configuring virtual systems.UTM
 |
| Image credit: UTM |
UTM is a free and open-source QEMU-based virtualization and emulation software for iOS and macOS (available only for Apple platforms). It supports +30 processors, including x86_64, ARM64, and RISC-V. Additionally, UTM offers a variety of features, including JIT-based acceleration, macOS VM creation (Virtualize macOS), and QXL/SPICE graphics mode.
🗨 What virtualization software are you currently using? Do you know a software that you think should be on the list?
If you enjoy reading my blog and want to support it: Paypal account: contact@linuxtechmore.com. For more support options contact me.{alertIdea}

